Product Overview
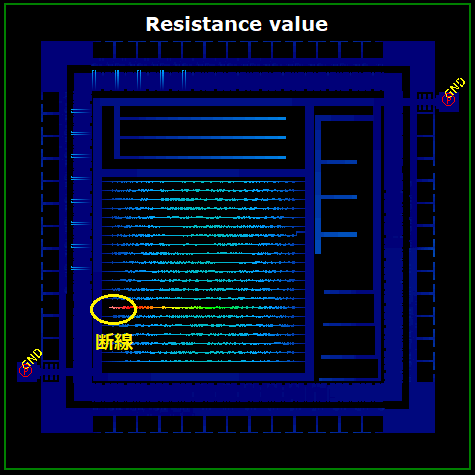
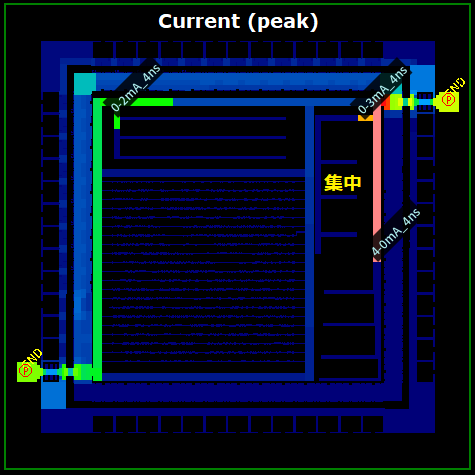
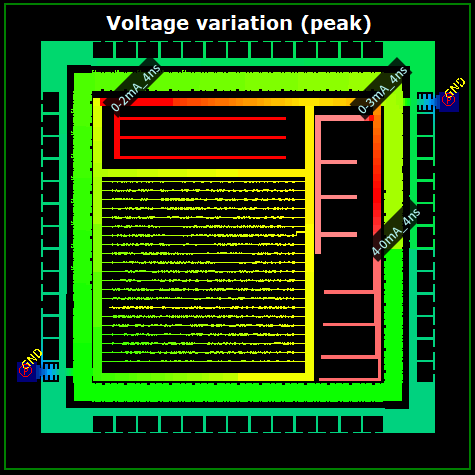
RSCALC is a "resistance value calculation & analysis tool" that provides intuitive verification of point-to-point R, and calculations of current density, current value, and voltage. The results of calculations can be displayed as a color (distribution) map on IC Design Visualization tool LAVIS-plus and be checked visually.
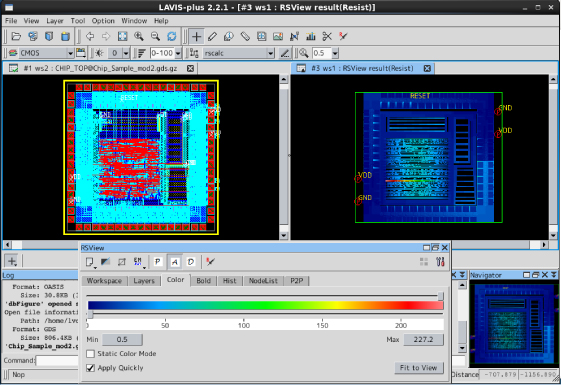
- Quick resistance value calculation achieved by original calculation method and multi-threading.
- No need for netlist, and power/ground routing can be checked early in design phase.
Operating Environment
| OS | Version | Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Linux | RedHat Enterprise Linux 7 and 8, and OSs compatible with these versions | x86_64 (64bit) |
Main Features
Wire length calculation and displayWire length from pad is calculated and displayed in color mapping where the shortest path is also displayed on demand. |
Allowable current and current density calculation and displayBy replacing wire width with allowable current value and displaying in color mapping, high resistance portions can be and identified by color-mapping wire widths. Also, color mapping differences over adjacent figures provides you with on-the-fly identification of idiosyncratic change of allowable current value induced by drastic wire-width changes. |
and more...